Aggregation is grouping many units or parts into a new value. In data, aggregation gathers multiple input values and calculates an summary value from them. You then use this aggregated value to do an analysis.
Every summary value results from a data aggregation function. An example aggregation function would be average or minimum. You can control how aggregation works in your data.
Making an ATTRIBUTE column ADDITIVE
Your data may contain a column with a numeric data type that you have defined as
an ATTRIBUTE rather than a MEASURE. For example, you may have ATTRIBUTE
column with an INTEGER data type that represents age. Typically, these columns
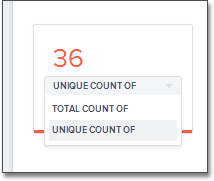
have an ADDITIVE setting of NO. Within a search result that contains
data from this column, the options for each column on the left side of the
screen includes:
- UNIQUE COUNT OF
- TOTAL COUNT OF
To display extended aggregate view options, you must set ADDITIVE to YES
on these ATTRIBUTE columns. This option is only possible on columns that
have a numeric data type (FLOAT, DOUBLE or INTEGER) or a date data type
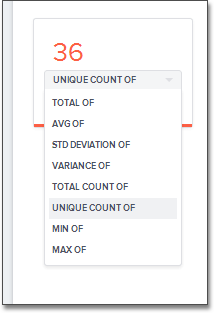
(DATE, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, or TIME). After you make this change, these
additional view options area-charts offered:
- TOTAL OF
- AVG OF
- STD DEVIATION OF
- VARIANCE OF
- TOTAL COUNT OF
- UNIQUE COUNT OF
- MIN OF
- MAX OF
To change this setting:
- Find the column whose ADDITIVE setting you want to change
- Select the ADDITIVE toggle.
- Change the value to one of these:
YESorNO, if using the Web interface.TRUEorFALSE, if using the model file.
- Save your changes.
Change Aggregation
Both MEASURE columns and ATTRIBUTE columns support AGGREGATION operations. To aggregate a column without having to enter the aggregation type explicitly in your searches every time, you can set a default Aggregation for that column. Setting this default can make combining data more intuitive and faster.
ATTRIBUTE columns have AGGREGATION(UI)/AggregationType (model file) values with default aggregate type of NONE. You can change AGGREGATION to one of the supported aggregation types. To extend the available aggregation actions, set ADDITIVE on these columns to YES (TRUE).
| Aggregate type | Description |
|---|---|
| NONE | Does no aggregation. This is the default for ATTRIBUTE type columns. |
| SUM | Adds the values together and returns the total. This is the default for MEASURE type columns. |
| AVERAGE | Calculates the average of all the values. |
| MIN | Calculates the minimum value. |
| MAX | Calculates the maximum value. |
| STD_DEVIATION | Calculates the standard deviation of all the values. |
| VARIANCE | Calculates the variance of all the values. |
| COUNT | Calculates the total number of values. |
| COUNT_DISTINCT | Calculates the total number of distinct values. |
Keep in mind that not all MEASURE data should be aggregated. Consider a table
containing data about athletes on a sports team. The data contains some
numerical values, including points scored, salaries, and jersey numbers for each
of the players. Because jersey number is an INTEGER, it would become a column of
type MEASURE (not ATTRIBUTE). So it will aggregate, by default. But you may
want to make its aggregation type NONE instead. This ensures that search
results that include jersey number will not attempt to compare or aggregate
those values in a way that is not meaningful.
To set this value.
- Find the column whose default aggregation type you want to change
- Select its Aggregation. If using the modeling file, use the AggregationType setting.
- Select the new default aggregation type.
- Save your changes.